In my previous post, I have described the types of environment variables, how to add the environment variable manually in the UFT Environment tab and directly at any step in the code itself.
In this blog post, I am going to explain the following things on External Environment Variables that can be used appropriately to develop better automation test scripts and enhance the automation framework.
Loading User-Defined external environment variables into UFT Manually
I have created an XML file having two environment variables(URL, ToolName) as follows:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
<Environment> <Variable> <Name>URL</Name> <Value>https://myskillpoint.com</Value> </Variable> <Variable> <Name>ToolName</Name> <Value>UFT</Value> </Variable> </Environment> |
Now go to the File>Settings and select the Environment menu from the Test Settings window. Select user-defined from Variable type drop-down and click on the select the checkbox “Load variables and values from external file” to enable the browse button.

Browse the TestEnvVariable.xml file and click on the OK button. A dialog will be displayed to convert the file path into a relative path. Click on the Yes button. The environment variables will be loaded in the user-defined variable list.
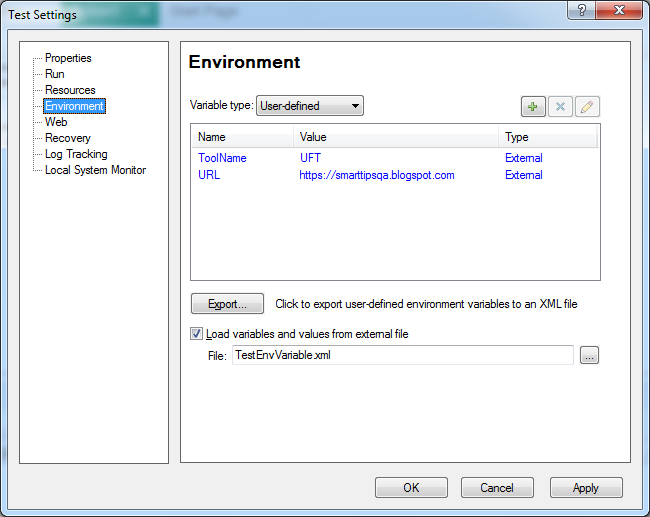
Now you can use these environment variables anywhere in your automation scripts or functions. One important thing is to be remembered here is that you can’t modify the value of this external user-defined at runtime because they will be available as read-only variables during the script execution.UFT will through an error message at runtime if you erroneously try to modify the value of an external environment variable.
Loading user-defined external environment variables into UFT dynamically
It’s quite simple to dynamically load user-defined external environment variables into UFT.
1. Create an XML file containing environment variables.
2. Write the following line in your test script.
|
1 |
Environment.LoadFromFile "E:\UFT_WorkSpace\Environment Variables\TestEnvVariable.xml" |
Exporting user-defined External Environment variables manually
Getting the name of the external environment variable file name at runtime
|
1 2 3 |
strEnvVarName = Environment.ExternalFileName Msgbox strEnvVarName |
The name of the external environment variable file name will be displayed in the message box.

How to use the user-defined External environment variables
There could be various scenarios where user-defined .environment variables can be used. I am providing a few examples.
- A function or an action is generating an output value that has to be used in many places, in that case, you can define the environment variable in the code itself and used it wherever required.
- You are developing an automation framework and you are using some external files like MS Access Database to store your test data and a configuration file to store some config details. If you think that the path of the required files might change in the future or it might be different for every user as per their directory structure, in that case, you can manually define the environment variables in Environmental Tab to store the path of the required files that anybody can change from TestSettings rather than doing any change in the code.
Recommended Posts
- Read, Write and Update Excel File In UFT
- How To Use Dictionary Object in UFT With Examples
- Find a Matching Pattern in String Using Regular Expression in UFT4
- How to Use Function Definition Generator in UFT
- Examples of Reporter.ReportEvent in UFT
- GetRoProperty , SetToProperty & GetToProperty in UFT With Example
- How to Use XPath in UFT One To Identify Web-Based Objects
- VBScript Loops in UFT
- Read and Update XML File in UFT | VBA
- VBScript MySQL Database Connection in UFT



