In VBScript Error Handling is mechanism to handle unwanted exceptions that might break the execution of code leading to failure of the script. So, exception handling plays a very crucial role in writing a robust scripts so that if any error occurs at runtime, the programme keeps executing the next steps even after the occurrence of errors.

If you are writing automation scripts in UFT, you must handle exceptions appropriately so that the Test Suite that is usually executed at daily nightly batch in unattended mode don’t get stuck due to any runtime exception.
Types of Errors in Programming
Before understanding the concept of error handling, first of all you must know what are the types error in a programming language.
There are three types of errors in any programming language.
- Syntax Errors
- Runtime Errors
- Logical Errors
Syntax errors
Syntax errors cause parsing errors and are caught before VBScript code execution. A few examples of syntax errors are incorrect function names, unbalanced strings (like missing an opening or closing parenthesis, missing double quotes) and etc.
Example: The following code causes syntax error due to missing double quotes while assigning value to myVar.
|
1 2 3 |
Dim myVar myVar = "MySkillPoint ' Cause a syntax error as it has missing double quote |
Runtime Errors
Runtime errors arise only during execution and are not detectable during code parsing. This is why they are also known as exceptions.
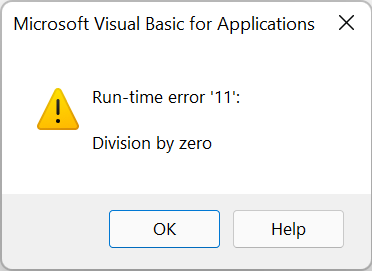
Example: The following code is perfectly fine and has no syntax errors. However, because we can’t divide an integer by 0, we’ll get a runtime error during execution, and the code will crash.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
Dim myVar, i i = 25 myVar = i / 0 'will cause runtime error Msgbox "Division Result is: " & myVar |
Logical Errors
Logical errors means, you have written a code but you are not getting the expected outcome. In such situation you have to debug your code where you are making a mistake.
VBScript Error Handling Techniques
We will see how to use the following methods to catch exceptions / errors in VBScript at runtime.
- On Error Resume Next
- Err Object
- On Error GoTo 0
On Error Resume Next
The name of this method is self-explanatory: if an error occurs, resume the flow of execution to the next line of the script.
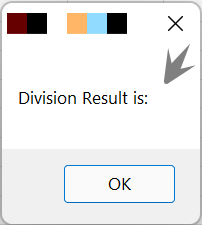
Example: We will again divide a number by 0. However, this time, the code will crash and proceed to next line and display the outcome in the message box.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
Dim myVar, i On Error Resume Next 'Using Error handling Statement i = 25 myVar = i / 0 MsgBox "Division Result is: " & myVar ' Value of myVar will not be displayed in message box owing to error divisible by 0 |
Err Object
This technique is most commonly used to retrieve the Error’s details so that you can write your logical code based on it if you know well in advance that an exception might occur at a particular step.
Err.Number ‘ Returns the Error Number
Err.Description ‘ Returns the Error Description
Err.Clear ‘ Clears the Error
Example: The following example shows how to use Err object.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
Dim myVar, i On Error Resume Next 'Using Error handling statement i = 25 myVar = i / 0 If Err.Number <> 0 Then ' If an Error Occurs MsgBox "Error Number is: " & Err.Number & " and its Description is: " & Err.Description Err.Clear '(It will Clear the Error) End If On Error GoTo 0 ' Disabling Error Handler |
On Error GoTo 0
This statement does not handle error instead it is used to disable any error handler in the script. This will set the handler to null value or Nothing, indicating that the script will no longer support error handlers. The same has been shown in the above example.
Conclusion
I hope you’ve gained a good knowledge of Error Handling in VBScript from this tutorial. If you liked this content, please share it with your friends.



